Mobile Testing
Mobile Testing can be defined as the process of testing the mobile devices to check the performance of developed software application usability, functionality and consistency. The Mobile App Testing can be done through either manually or automatically.
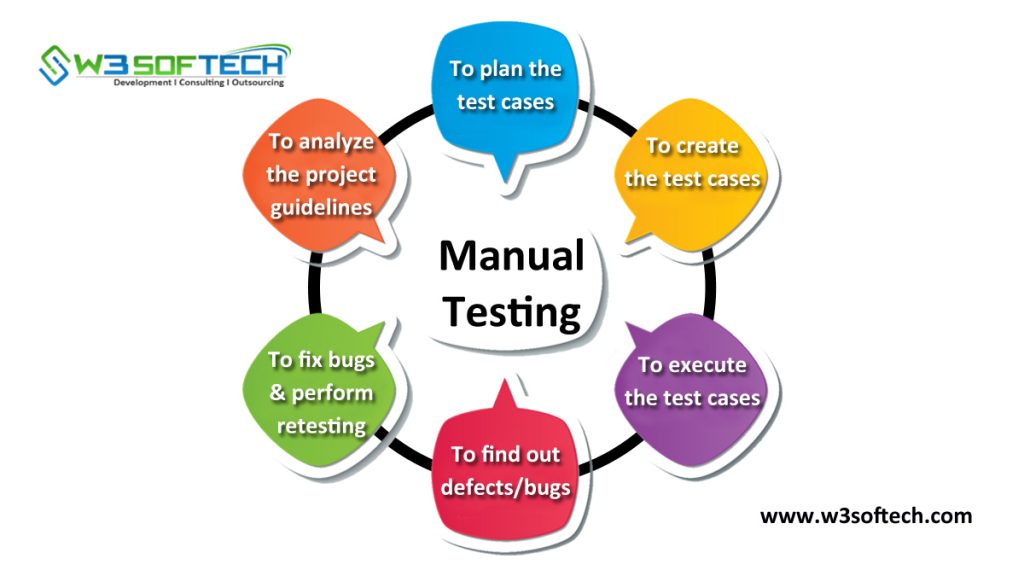
Mobile Testing Types:
Mobile Application Testing can be divided into two types namely Software Testing and Hardware Testing
Software Testing:
The process of testing the software application developed for mobile devices is known as Mobile Software Testing or Mobile Application Testing. Again this testing is divided into three parts
Native Apps: Native apps are apps created for general purpose usage on mobile platforms and tablets.
Mobile Web Apps: These apps are called server-side apps developed to access websites on mobile using various browsers such as Firefox, Chrome, etc.,
Hybrid Apps: These are the combination of the above two apps which can run on offline as they are developed using HTML5 and CSS
Hardware Testing:
This testing is used to perform on hardware parts of devices like internal processors, screen sizes, resolution, RAM, ROM, camera, Bluetooth, FM Radio, etc.,
Differences between Native Apps and Mobile Web Apps:
| Native Apps | Mobile Web Apps |
| It has a single platform affinity | It has a cross-platform affinity |
| These are written in SDK format | These are written in HTML, CSS, PHP, etc., |
| Only downloadable from play store or app store | Only accessible through the internet |
| It requires installation compulsory | No need for any installation |
| Can be updated from play store or app store | These are centralized updates |
| Most of the native apps don’t need an internet connection | For all mobile web apps, the internet is compulsory |
| Works faster | Works based on web technology used |
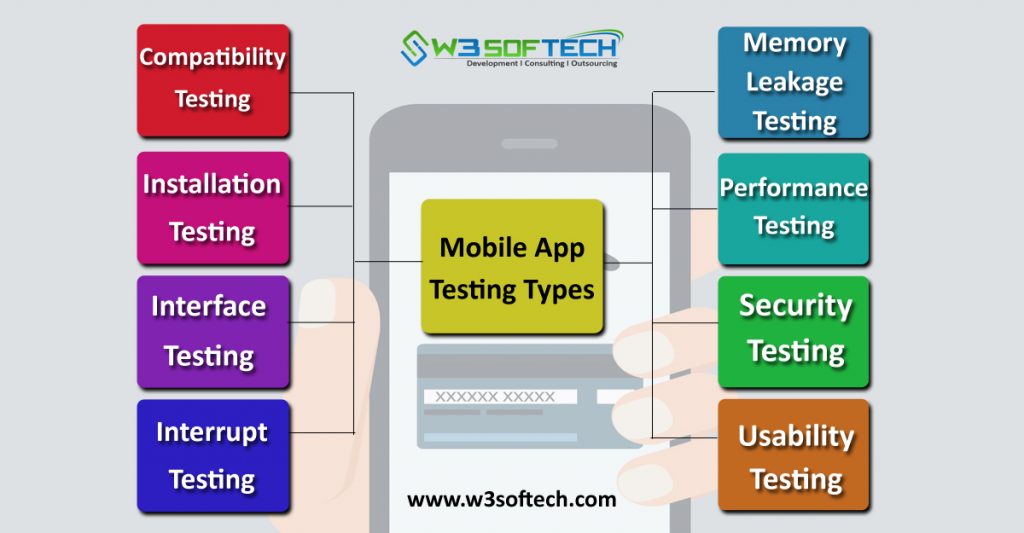
Types of Mobile Testing:
Depending on the mobile testing types, below are the testing types which are used to perform on mobile devices
Usability Testing:
The name itself says that it is used to check the user experience of the developed mobile application. It should satisfy the user in terms of usability, flexibility and friendliness
Compatibility Testing:
This testing is usually performed on mobile devices to make sure that whether the developed mobile application is comfort with the device. To check that the developed app is compatible with mobile’s screen resolution, OS Versions, etc.,
Interface Testing:
Interface Testing helps to determine the performance of user interface like menu buttons, history, settings, bookmarks, etc.,
Interrupt Testing:
Interrupt Testing is the process of testing an application which may undergo interruption while using the mobile app. In simple words we can say that testing the developed mobile app while there may come interruptions like SMS, Calls, Web notifications, on/off the media player, etc. ,
Memory Leakage Testing:
It helps to determine the optimization of the mobile app under limited memory. Thus, each developed application should work without making any memory leakage and satisfy the user.
Performance Testing:
Testing the performance of a mobile application which may go under various changes like data changes from mobile to wifi, low battery power consumption, network coverage, etc., Here testers need to perform testing on both sides of application such as server-side client side.
Operational Testing:
Operational Testing is the process of testing a mobile application’s backup or recovery functions if the user upgraded an app from a store.
Installation Testing:
Whenever a user is able to install, uninstall or upgrade the developed app this testing came into existence. The mobile app should satisfy the user while performing any of the above steps without interrupting.
Security Testing:
Security Testing is the process of testing to determine the security of the mobile app without losing any data. Here testers need to check the app whether it is working under given security guidelines and protecting the data.
 |
| Mobile Testing Types - W3Softech |
| Mobile App Testing | Desktop Testing |
| The developed software application can be tested on mobile devices like Samsung, Apple, Nokia, etc., | Here the application is tested on a Central Processing Unit (CPU) |
| Mobile devices consist of low screen resolution | Desktop consists of high screen resolution |
| Mobile devices contain less internal memory | The desktop contains a large amount of internal memory |
| Here they use network connections like 2G, 3G, 4G or Wi-Fi | Whereas desktop use dial-up or broadband connections |
| Automation Tool may not work properly on mobile apps | Automation Tool will work properly on desktop testing |
Mobile App Testing Tools:
These are the top 16 mobile app testing tools
- Appium
- Appium Studio
- Calabash
- Frank
- FrogLogic
- KIF
- KMAX
- Kobiton
- MonkeyRunner
- MonkeyTalk
- Robotium
- SeeTest
- Selendroid
- SmartBear
- Testdroid
- WebLoad